Asthma is a long-term condition that causes the airways in the lungs to narrow and swell. It is often triggered by viruses, allergens, exercise, and certain medications. Some people have intermittent symptoms while others experience them on a regular basis.
Symptoms
Coughing is the main symptom of asthma. It can happen at any time, but it is often worse when you are active or upset. It can last for several minutes or longer, and may be accompanied by wheezing or shortness of breath. Asthma can also cause a feeling of tightness in the chest. It can make it difficult to talk or sing, and may result in a bluish color around the lips, which is called cyanosis. It is important to treat the symptoms of asthma, as they can cause serious problems if left untreated over time.
There are many different types of asthma, and the symptoms can vary in severity. Some people have mild asthma, with symptoms occurring rarely or only during exercise. Others have symptoms almost every day, or all the time. It's important to see a health care provider if you or your child has symptoms more than twice a week, especially when they occur at night.
If your child has a severe asthma attack, it can be life-threatening. It is important to follow the emergency instructions in your asthma action plan if this happens. This includes using an epinephrine pen, if your child has one. Patients with asthma have frequently recommended various medications; one such lifesaver is the Asthalin Inhaler. Follow the directions on the pen, and call 911 if needed.
Some factors can increase a person's risk of developing asthma, including family history of the disease (especially among siblings); having other allergies, such as hay fever; and living in an area with high levels of pollution or irritants, like cigarette smoke or chemical fumes. Boys are more likely to develop asthma than girls, but the condition can affect people of any gender and age.
Asthma can be treated with medicines that reduce inflammation in the lungs, such as corticosteroids, or quick-relief medicines that stop symptoms when they start. You will usually need both kinds of medicine, and your health care provider may change the type or dose of your medicines as your condition changes. It is also important to identify what triggers your symptoms, and try to avoid them or limit contact with them as much as possible.
Triggers
A person with asthma has swollen (inflamed) and sensitive airways that become narrow and clogged with sticky mucus in response to certain triggers. These triggers are different for every person with asthma. They can be things like smoke, pollens, mold spores, animal dander, cold air, and chemicals from cleaning products or perfumes. Other triggers can include stress and strong emotions, such as anger or fear. Certain occupational exposures can also be triggers, especially if they involve breathing in fumes or dust.
When a person with asthma is exposed to a trigger, their immune system responds by sending cells to the area to fight the trigger. This causes the airways to tighten, causing wheezing and coughing. They may need to take their rescue inhaler to start breathing normally again.
Many people with asthma have allergies as well. Allergies can make asthma worse by causing the body to produce extra antibodies against common allergens, such as tree, grass and weed pollens; mold; animal dander; cockroach droppings; and dust mites. It's important to see an allergist for allergy testing and treatment, as this can help improve the control of asthma.
It's also important to understand what triggers your asthma symptoms, so you can avoid them. When included in a comprehensive treatment regimen, Levolin Inhaler enhances supportive asthma control. Long-term monitoring of adverse effects ensures adjustments for the best results. Some triggers are under your control, such as exercise and cold air. Other triggers are harder to avoid, such as viruses or respiratory infections.
Symptom triggers, such as coughing or wheezing, may occur even when the air is clear. This is because the lungs have to work harder when they're inflamed. Other symptoms may be caused by the medication used to treat asthma, or by gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD; when the stomach contents back up into the esophagus) and excess weight.
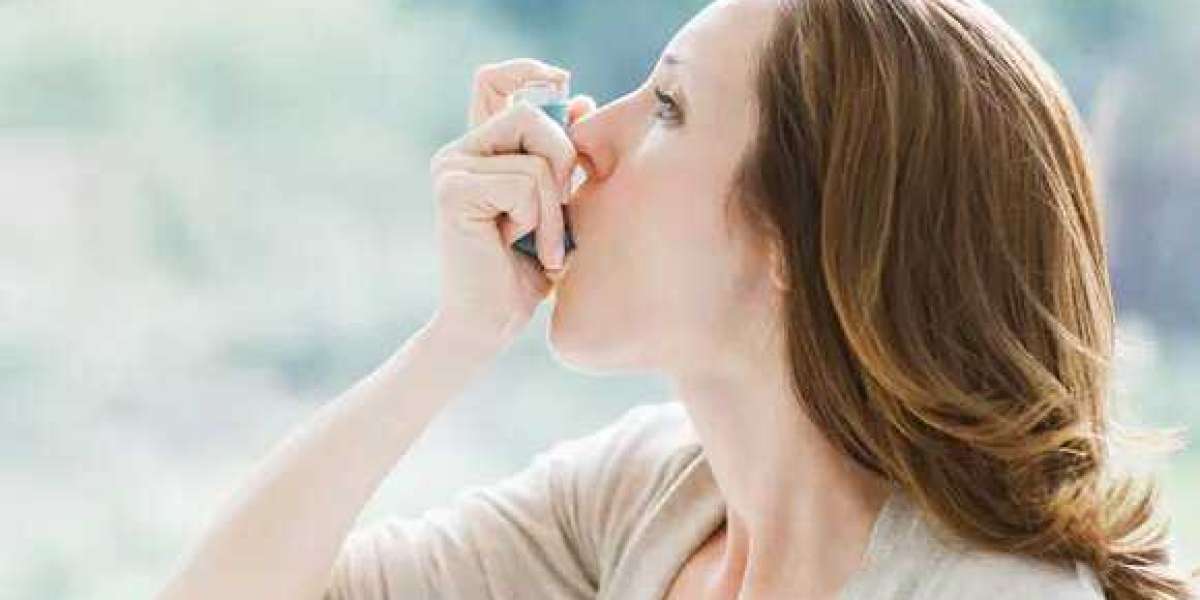
In addition to working with an allergist, it's important to learn how to use your inhaler correctly. This can help the medicine get down to the lungs more easily. Our inhaler technique videos show you how to do this. Another thing you can do is to stop smoking and avoid secondhand smoke, because it's a known asthma trigger. The same goes for pets.
Treatment
Asthma can be controlled by medicine that reduces swelling and inflammation of the airways and helps your body resist attacks. Your doctor may also recommend other treatment such as a special diet, breathing exercises or supplements. The most important treatment is taking your medicine regularly and properly, not missing doses or stopping them early. You should also follow your action plan if your symptoms get worse, as this will help you know what to do next.
Your GP or asthma nurse will talk to you about what type of inhaler you have and how to use it. They will give you a asthma action plan that tells you what to do in different situations and what to do if your symptoms are getting worse or not getting better. The action plan should be reviewed every four to eight weeks or whenever you change your medicines.
Most people with asthma take long-term control medicine (also called steroids) to prevent attacks. This is taken daily and should not be stopped unless your doctor says to do so. You may also need a quick-relief inhaler to treat an attack.
Short-acting beta-adrenergic drugs can help relieve sudden symptoms by opening the airways. These medicines are called bronchodilators and work by stimulating receptors on the cells in the lungs. They act within minutes, but their effects last only 2 to 6 hours. They can be used with a spacer device, which allows more medicine to enter the lungs, or without one.
People with mild asthma often do not need this medication. But it is important for people with moderate to severe asthma to use it regularly. It can stop an asthma attack in its tracks and is the only thing that can save a life in case of a severe asthma attack.
It is important to use a spacer device with your inhaler, as this will get more medicine into your lungs. The device has a holding chamber that you place the mouthpiece of your inhaler into. Close your lips tightly around the mouthpiece and then inhale slowly and steadily through your mouth. If you can’t fit your entire breath into your mouth, inhale through the mouthpiece again until you have breathed in as much as you can.